频域滤波
频域滤波是在频率域对图像做处理的一种方法。步骤如下:
滤波器大小和频谱大小相同,相乘即可得到新的频谱。
滤波后结果显示,低通滤波去掉了高频信息,即细节信息,留下的低频信息代表了概貌。常用的例子,比如美图秀秀的磨皮,去掉了脸部细节信息(痘坑,痘印,暗斑等)。高通滤波则相反。
高通/低通滤波
1.理想的高/低通滤波
顾名思义,高通滤波器为:让高频信息通过,过滤低频信息;低通滤波相反。
理想的低通滤波器模板为:
其中,D0表示通带半径,D(u,v)是到频谱中心的距离(欧式距离),计算公式如下:
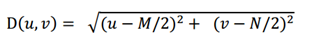
M和N表示频谱图像的大小,(M/2,N/2)即为频谱中心
理想的高通滤波器与此相反,1减去低通滤波模板即可。
部分代码:


# 定义函数,显示滤波器模板 def showTemplate(template): temp = np.uint8(template*255) cv2.imshow('Template', temp) return # 定义函数,显示滤波函数 def showFunction(template): row, col = template.shape row = np.uint16(row/2) col = np.uint16(col/2) y = template[row, col:] x = np.arange(len(y)) plt.plot(x, y, 'b-', linewidth=2) plt.axis([0, len(x), -0.2, 1.2]) plt.show() return # 定义函数,理想的低通/高通滤波模板 def Ideal(src, d0, ftype): template = np.zeros(src.shape, dtype=np.float32) # 构建滤波器 r, c = src.shape for i in range(r): for j in range(c): distance = np.sqrt((i - r/2)**2 + (j - c/2)**2) if distance < d0: template[i, j] = 1 else: template[i, j] = 0 if ftype == 'high': template = 1 - template return template
Ideal
2. Butterworth高/低通滤波
Butterworth低通滤波器函数为:
从函数图上看,更圆滑,用幂系数n可以改变滤波器的形状。n越大,则该滤波器越接近于理想滤波器
1减去低通滤波模板即可得到高通滤波模板
部分代码:


# 定义函数,巴特沃斯高/低通滤波模板 def Butterworth(src, d0, n, ftype): template = np.zeros(src.shape, dtype=np.float32) # 构建滤波器 r, c = src.shape for i in np.arange(r): for j in np.arange(c): distance = np.sqrt((i - r/2)**2 + (j - c/2)**2) template[i, j] = 1/(1 + (distance/d0)**(2*n)) # Butterworth 滤波函数 template[i, j] = np.e ** (-1 * (distance**2 / (2 * d0**2))) # Gaussian滤波函数 if ftype == 'high': template = 1 - template return template
Butterworth
3. Gaussian高/低通滤波
Guassian低通滤波器函数为:
1减去低通滤波模板即可得到高通滤波模板
部分代码:


# 定义函数,高斯高/低通滤波模板 def Gaussian(src, d0, ftype): template = np.zeros(src.shape, dtype=np.float32) # 构建滤波器 r, c = src.shape for i in np.arange(r): for j in np.arange(c): distance = np.sqrt((i - r / 2) ** 2 + (j - c / 2) ** 2) template[i, j] = np.e ** (-1 * (distance ** 2 / (2 * d0 ** 2))) # Gaussian滤波函数 if ftype == 'high': template = 1 - template return template
Gaussian





















 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫



